Myocarditis
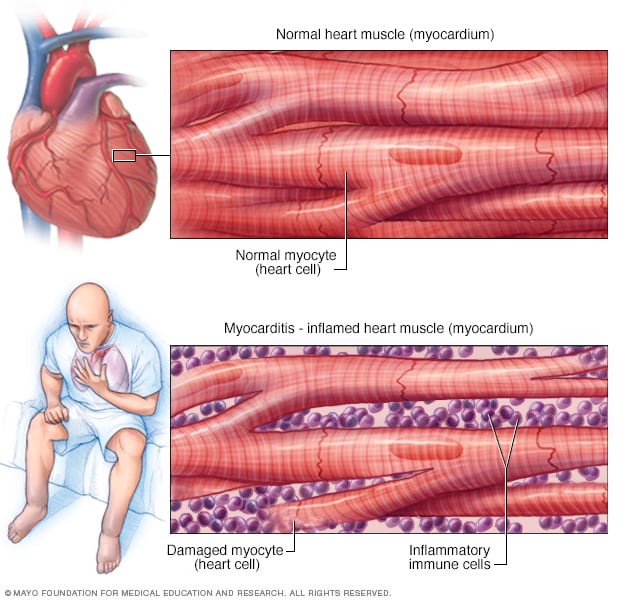
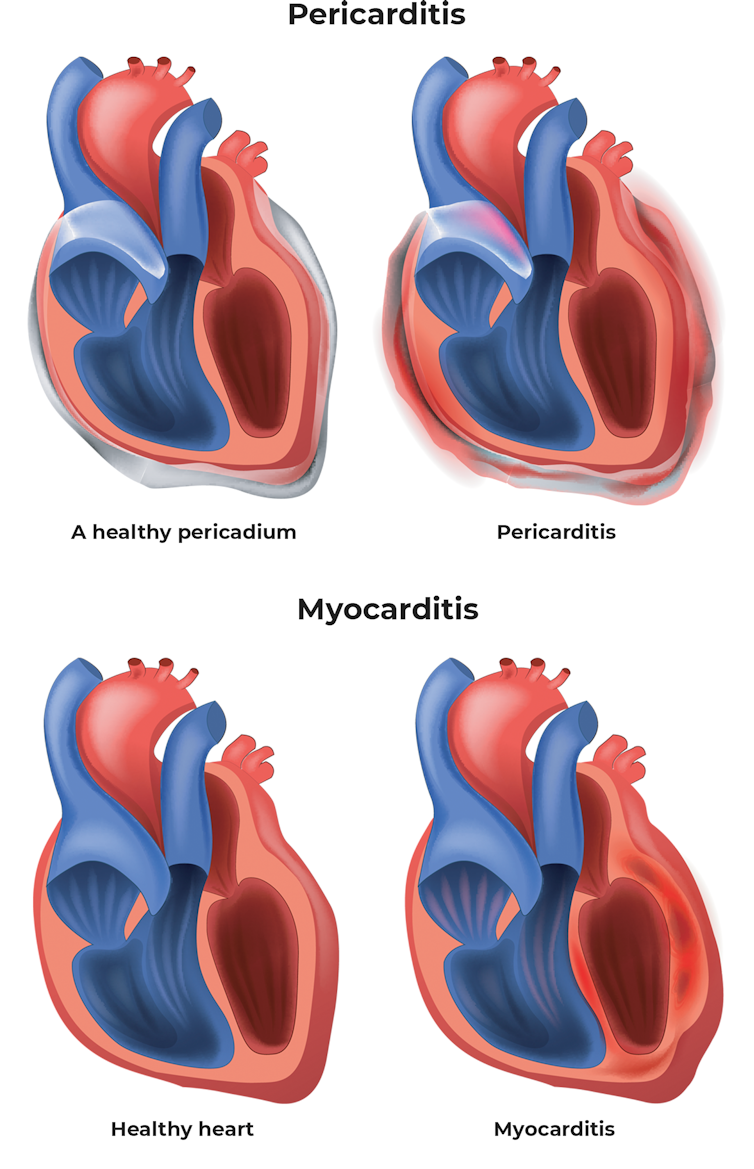
May present as fulminant acute or chronic myocarditis. Myocarditis is clinically and pathologically defined as inflammation of the myocardium Despite its rather clear-cut definition the classification diagnosis and treatment of myocarditis continue to prompt considerable debate.
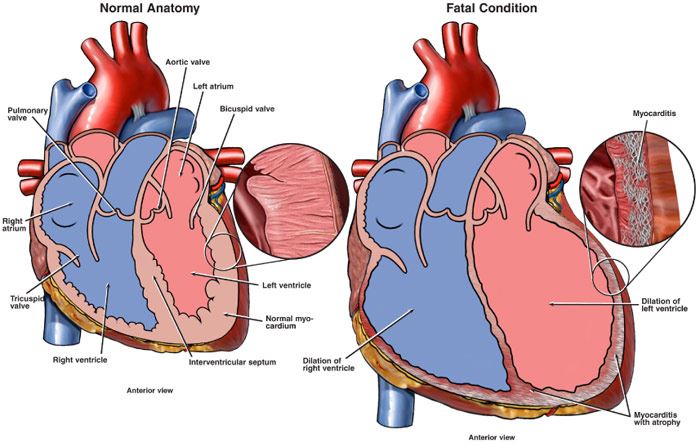
The fate of acute myocarditis between spontaneous improvement and evolution to dilated cardiomyopathy.

Myocarditis. It is important to note however that. Myocarditis can be produced by a variety of infectious and noninfectious causes. While its usually caused by an infection it also can occur in people who suffer from autoimmune disorders.
Importantly myocarditis is also a possible complication of COVID-19. Its true 397 cases of myocarditis were reported after around 89 million adolescents who got the vaccine. ATAGI and CSANZ emphasise that the overwhelming benefits of vaccination using an mRNA vaccine in protecting individuals against COVID-19 and its serious outcomes such as hospitalisation and death.
Consider myocarditis and pericarditis in adolescents or young adults with acute chest pain shortness of breath or palpitations. Most often myocarditis results from. Dilated cardiomyopathy with chronic heart failure is the major long-term sequela of myocarditis.
3618 Pan et al. Can affect all age groups with an apparent slightly higher incidence in males than females and equal incidence in black people and white people. Work-up with a respiratory viral panel was negative for both patients and the panel includes the most common viruses that cause myocarditis in the general population most notably adenovirus and coxsackie virus.
There were 14 deaths in children aged 12 to 17 who had the Pfizer Covid-19 vaccine. A CDC study on 12 to 17 year-olds who got the Pfizer vaccine found 397 reports of heart inflammation. Myocarditis or inflammation of the heart muscle is uncommon but can be life-threatening if left untreated.
Dtsch Arztebl Int 2012. It can affect anyone at any age and is usually related to recent viral infection. The virus may have gone but the immune system over-reacts causing inflammation that can persist in the heartOther causes include bacterial infections certain.
In addition to myocarditis coronavirus infection was also associated with an increased risk of heart attacks irregular heart beat blood clots in the lungs or legs kidney injury and bleeding. The more routine use of endomyocardial biopsy has helped to better define the natural history of human myocarditis and to clarify clinicopathological. In the reported COVID-19 cases with myocarditis in the literature clinical presentations have varied.
Myocarditis and pericarditis due to a variety of causes are also commonly seen in the general population. Getting an accurate diagnosis is vital as treatments for autoimmune-related myocarditis. It can be an acute subacute or chronic disorder and may present with focal or diffuse involvement of the myocardium.
If the myocarditis in these two cases was related to an immune response this could explain why it occurred after the second dose in both cases. In the United Kingdom one young person dies suddenly each week due to undiagnosed myocarditis. Inflammatory cardiomyopathy is defined as myocarditis in association with cardiac dysfunction and ventricular remodelling 12Despite extensive research and improved diagnosis and understanding of.
Myocarditis means inflammation of the heart muscle. Treatment is usually supportive. Ask about prior COVID-19 vaccination if you identify these symptoms as well as relevant other medical travel and social history.
Myocarditis is an inflammatory disease of cardiac muscle that is caused by a variety of infectious and noninfectious conditions table 1 1. For initial evaluation consider an ECG. In this younger population coronary events are less likely to be a source of these symptoms.
Established myocarditis is a relatively rare sequelae of COVID-19 infection. Myocarditis early biopsy allows for tailored regenerative treatment. There is potential overlap in symptomatology in patients with primary COVID-19 infection and COVID-19 patients with clinically suspected myocarditis.
Diagnostic Performance of Extracellular Volume Native T1 and T2 Mapping Versus Lake Louise Criteria by Cardiac Magnetic Resonance for Detection of Acute Myocarditis. Myocarditis may present with a wide range of symptoms ranging from mild dyspnea or chest pain that resolves without specific therapy to cardiogenic shock and death. Myocarditis describes a heterogeneous group of disorders characterised by myocardial inflammation in the absence of predominant acute or chronic ischaemia.

Myocarditis Causes Symptoms Treatments British Heart Foundation

Myocarditis In A Patient With Covid 19 A Cause Of Raised Troponin And Ecg Changes The Lancet
The Benefits Of A Covid Vaccine Far Outweigh The Small Risk Of Treatable Heart Inflammation
Possible Link Between Pfizer And Moderna Mrna Vaccines And Rare Heart Inflammation Under Investigation Abc News
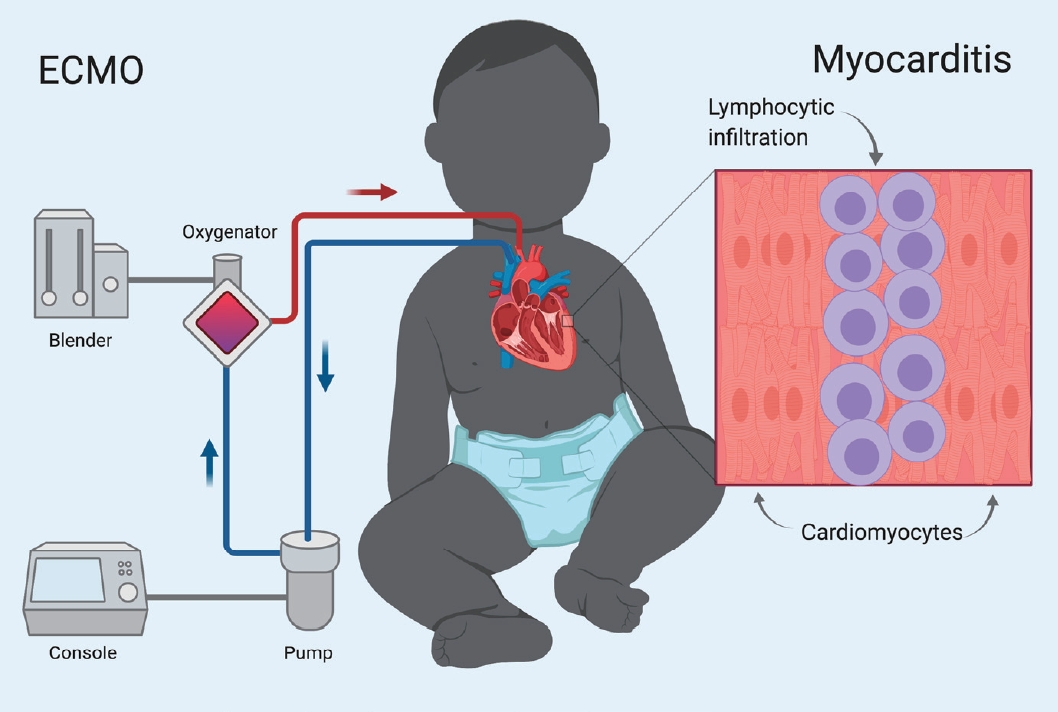
The Use Of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation In Children With Acute Fulminant Myocarditis
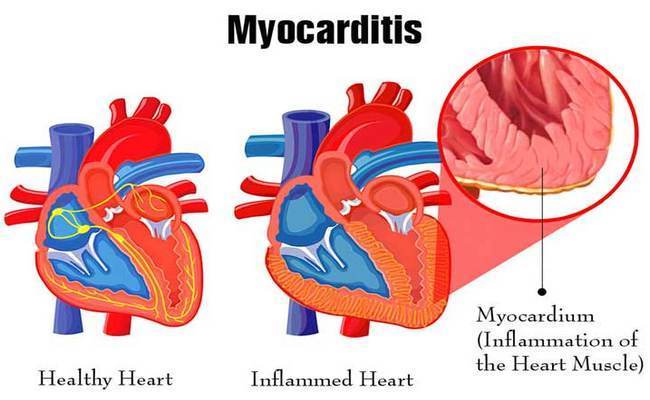
Guide To Myocarditis A Dangerous Heart Condition Affecting Up To 78 Percent Of Covid 19 Infected Symptomatic Or Asymptomatic Individuals Thailand Medical News

Myocarditis In A 16 Year Old Boy Positive For Sars Cov 2 The Lancet

Myocarditis Symptoms Causes Treatment Recovery Time
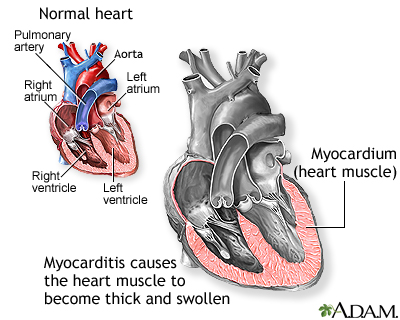
Myocarditis Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia
Myocarditis Risk From Mrna Covid Vaccines Re Evaluated In Canadian Study Research Now Withdrawn

Myocarditis Hartontstekingen Hartziekten Patient
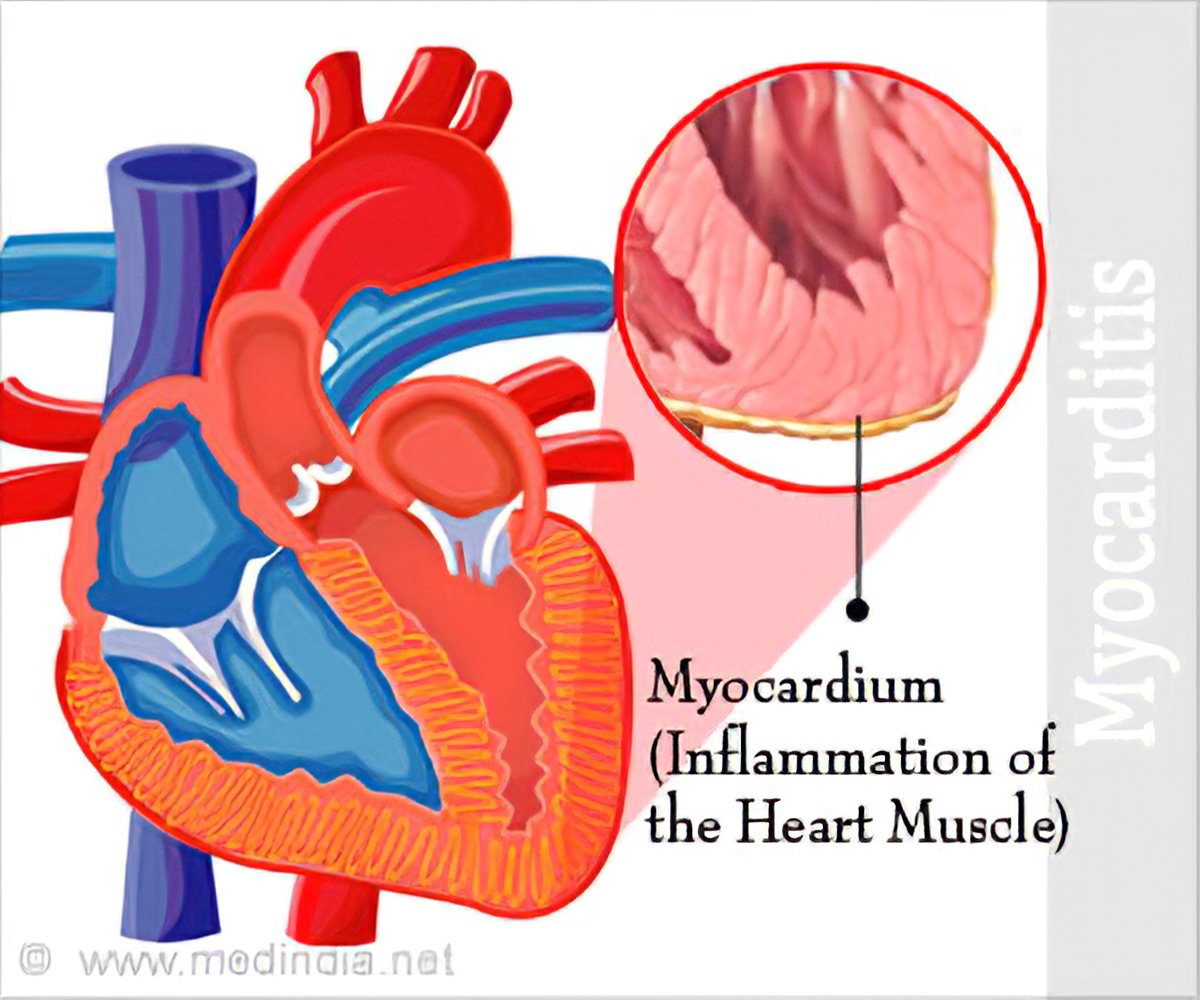
Myocarditis Types Causes Symptoms Complications Treatment Prognosis
Myocarditis Diagnosis Symptoms And Treatment

Recognizing Covid 19 Related Myocarditis The Possible Pathophysiology And Proposed Guideline For Diagnosis And Management Heart Rhythm